Foam generation and application using the FoamFatale method is not only the number one choice if fire extinguishing water is insufficiently available in hydrocarbon storage tank terminals. Large quantities of combustion residue and contaminated extinguishing water also need to be avoided for environmental reasons. This automatic and autonomous self-expanding foam system responds instantly if a fire is detected and needs no external water or energy supply. After activating the system, it only takes two minutes to cover the entire tank surface with a foam blanket.
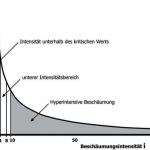
As shown in Figure 1, extinguishing times can be significantly reduced by increasing the foam application rate. The goal is to achieve superintensive foam flooding in order to reduce the air pollution from the fire to a minimum and at the same time avoid damage due to heat on the tank. Based on empirical measurements, it is possible to cut the extinguishing time to a few seconds. Short extinguishing times are important if a tank fire spreads over a large combustion surface.
In line with the existing guidelines for fire extinguishing systems, the extinguishing and foam application times in Figure 1 were determined by the low intensity values for the extinguishing time t and the foam intensity i. In order to obtain a shorter extinguishing time, established extinguishing strategies must be modified. The foam application time is an independent parameter whereas the foam intensity is a dependent variable that is adjusted to the size of the combustion surface. The first step towards extinguishing a fire is to generate the necessary foam thickness. With superintensive foam flooding this only takes a few seconds. The traditional static approach developed by the NFPA, for example, stipulates the same intensity value regardless of the combustion surface. If the intensity value is instead adapted according to the combustion surface, it can be seen that the bigger the surface, the greater the distance that has to be covered by the foam under the influence of the fire. The attacked foam surface is also larger as a result. The impact of the foam destruction can be more than offset by increasing the intensity and reducing the extinguishing time. A higher intensity value causes the foam to roll faster across the surface, so that it is only exposed to the drying, destructive effect of the fire for a short period of about ten seconds.
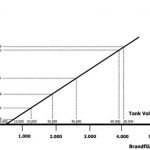
The second extinguishing phase entails increasing the foam blanket thickness. The amount of foam on the liquid surface needs to grow steadily until it is sufficiently thick. It is important to maintain the resistance and consistency of the foam, even if strong side winds could potentially open up a gap in the blanket. The higher intensity value results not only in a fixed foam application time, but also in a significantly higher safety factor. The values shown in Figure 2 are based on measurements and calculations of the foam spreading velocity for different tank sizes.
System design
The system is designed in two steps. In the first, the amount of foam required to size the container is determined. The method of foam supply depends on the chosen extinguishing strategy. The foam supply piping is sized in the next step. The upper limit for the foam application time is taken as a design basis. The crucial parameter is the time needed to apply a predefined total amount of foam to the tank on fire. With a stationary extinguishing system this is accomplished by a pressure vessel with premix foam. With a mobile system the premix foam is delivered by truck or trailer and connected to the extinguishing port on the tank. The maximum permissible foam application time is two minutes for a combustion surface of 2000 m² or three minutes for surfaces larger than 2000 m².
Foam application is the key
The foam intensity must be increased in order to extinguish the fire faster. To achieve this goal, the foam needs to be applied to the tank on fire at a high rate. Conventional foam ports or slides are unsuitable for handling the required quantity of foam. Since the foam is applied locally at a high velocity, the impact on landing swirls up the liquid hydrocarbon surface and submerges into the liquid, forming an emulsion.
The FoamFatale concept of curtain-like foam application increases fire extinguishing effectiveness in several ways:
- The consumption of extinguishing foam is reduced.
- The environmental impact is significantly lessened because the fire is extinguished in the shortest possible time and the surrounding areas are not contaminated.
- Minimal loss of product occurs.
- The tank shell is cooled, limiting the damage.
The efficiency of the FoamFatale technology has been proven in repetitive trials (without heat detection). Figure 3 shows snapshots of a 500 m² gasoline tank fire. The fire was extinguished after 40 s. The automated version will reduce the extinguishing time even further because the system will be activated immediately as soon as a fire is detected.
cpp 432
Share: